In the food industry, certain types of products require a cold chain. But what exactly is a cold chain, what are some examples, and why is it important to maintain a specific temperature? Let’s explore further. Cold chain food products are highly sensitive to temperature changes. These foods require special handling at low temperatures from the production process all the way to the consumer.
The primary purpose of the cold chain system is to maintain the quality, safety, and nutritional value of food, ensuring that products remain fresh and fit for consumption.
Contents
Why Do We Need Cold Chain Food Products?
There are several benefits why it is important to maintain a specific temperature for cold chain food products:
- Prevents Bacterial Growth: Low temperatures inhibit the growth of disease-causing bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria.
- Protects Nutritional Value: Vitamins and minerals in food are much more stable at low temperatures, preserving their nutritional value.
- Extends Shelf Life: Proper temperature control allows food to be stored longer without spoiling, preventing rot or changes in texture.
- Ensures Food Safety: The cold chain helps prevent food poisoning and foodborne illnesses.
- Maintains Organoleptic Quality: The right temperature preserves the taste, aroma, and appearance of food, keeping it delicious and appealing.
- Reduces Food Waste: By maintaining product quality, the amount of food wasted can be minimized.
- Improves Quality of Life: Access to fresh and nutritious food is enhanced.
Food Products That Require Cold Chains
Cold chain food products need special handling to maintain their quality and safety. By keeping the right temperature, we can enjoy food that is fresh, nutritious, and safe to consume. Here are some examples:
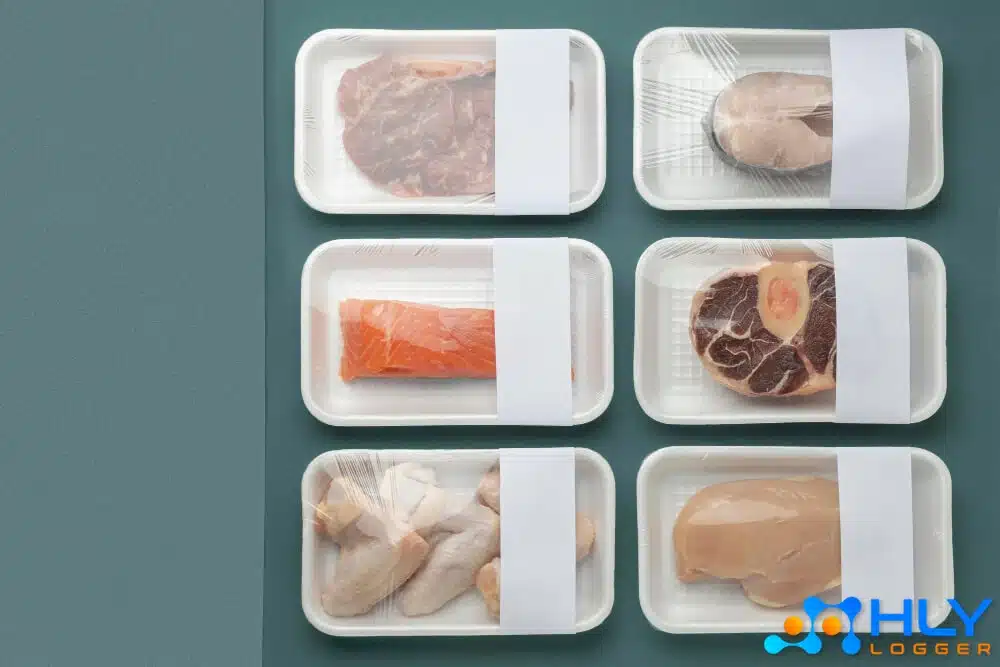
- Meat: Both red and white meat are highly susceptible to bacterial growth. Low temperatures help slow down the decay process and maintain freshness. Examples include fresh meat, processed meat, poultry, and other meat products.
- Fish and Seafood: Due to their high-water content, seafood is very perishable. Low temperatures help prevent bacterial growth and maintain a firm texture. Examples include fresh fish, shrimp, shellfish, and other seafood.
- Milk and Dairy Products: Milk and dairy products such as yogurt, cheese, and ice cream contain nutrients that are easily damaged by high temperatures. Low temperatures help preserve nutritional quality and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria like Listeria.
- Eggs: Fresh eggs and egg products are susceptible to contamination by Salmonella bacteria. Low temperatures help inhibit bacterial growth.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Certain fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries, grapes, lettuce, and spinach, are prone to wilting and rotting. Low temperatures slow down spoilage and maintain freshness.
- Frozen Foods: Foods that have been frozen must be stored at very low temperatures to maintain their quality. The freezing process halts microbial activity, allowing the food to be stored longer. This applies to frozen ready-to-eat foods like nuggets, frozen pizzas, and frozen seafood.
Cold Chain Distribution Process
The cold chain distribution process involves several stages:
- Production: Food products are produced while adhering to hygiene and safety standards.
- Cooling: Products are immediately cooled or frozen after harvest or production.
- Storage: Products are stored in refrigerated facilities such as cold warehouses or refrigerators.
- Transportation: Products are transported using refrigerated vehicles with controlled temperatures.
- Distribution: Products are distributed to various points of sale such as supermarkets, restaurants, or directly to consumers.
Challenges in Cold Chain Distribution
Several common challenges can arise in cold chain distribution, including:
- Temperature Fluctuations: Sudden changes in temperature can compromise product quality.
- Packaging Damage: Damaged packaging can lead to product contamination.
- Power Outages: Power failures can cause storage temperatures to rise.
- Distribution Distance: The farther the distribution distance, the greater the risk of product damage.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Cold Chain Products
When selecting cold chain food products, it is crucial to consider the following:
- Packaging: Ensure that the product packaging is intact, undamaged, and airtight.
- Expiration Date: Check the product’s expiration date before purchasing.
- Storage Temperature: Pay attention to the storage temperature indicated on the packaging.
- Product Origin: Choose products from reputable manufacturers who implement a good cold chain system.
Ultimately, cold chain food products require special handling to maintain their quality and safety, from harvest to consumption.