In this particular article, we will discuss about the wireless temperature sensors. The sensors measure ambient or object-specific temperatures and transmit the data to a receiver without the need for physical cables. Nowadays, everything is wireless right? For the sensors, there are many applications in various domains, including smart homes, industrial facilities, healthcare, environmental monitoring, offices, warehouses, and medical environments.
This products utilizes wireless connectivity—such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or radio-frequency communication—to measure temperature and send data wirelessly to a receiving device. In smart homes, for instance, wireless temperature sensors may be integrated into an IoT (Internet of Things) ecosystem to monitor temperatures in different rooms. In industrial settings, these sensors help maintain equipment and products within safe temperature ranges, while in healthcare and laboratory environments, they ensure proper storage conditions and patient safety.
Contents
How Wireless Temperature Sensors Work
Wireless temperature sensors typically operate as part of a larger system, which may include data recording, analysis, and integration with control mechanisms. For example, if the temperature drops below a preset threshold, the system can automatically activate a heater, maintaining a consistent temperature without manual intervention.
The operational sequence of wireless temperature sensors can be outlined as follows:
Temperature Measurement:
Wireless temperature sensors rely on components like thermistors, thermocouples, or semiconductor-based elements that detect temperature in their surroundings. These components convert temperature changes into electrical signals—such as a change in resistance for thermistors, or a change in voltage for thermocouples. While the sensing principle is similar to conventional wired sensors, the key difference is the ability to transmit data wirelessly.
Signal Processing:
Once the sensor detects a temperature change, it outputs an analog or digital signal. If the signal is analog, it passes through an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC), often integrated within a microcontroller, to produce digital temperature data. This data may be calibrated or processed to minimize noise and ensure accuracy, then converted into common units like Celsius or Fahrenheit.
Data Modulation and Preparation for Transmission:
Before sending the data wirelessly, the sensor’s embedded system modulates the digital signal into a form suitable for transmission over the chosen wireless communication medium. The modulation technique depends on the protocol—Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRa, or another wireless standard. This step ensures the temperature data can be carried reliably over the air.
Wireless Transmission:
The sensor transmits the modulated data via electromagnetic waves to a receiver, which could be a computer, smartphone, IoT gateway, or another control system. Different communication technologies and protocols ensure that data remains accurate and reaches its destination in real-time.
Data Reception and Interpretation:
The receiving device demodulates and decodes the signal back into digital data, then converts that data into readable temperature information. Users can view this information directly or the system can use it to trigger automated responses—such as adjusting a thermostat, sounding an alert, or activating cooling systems.
Advantages of Wireless Temperature Sensors Over Wired Sensors
Wireless temperature sensors offer several key benefits that make them a better choice for many modern applications:
Installation Flexibility:
Without the need for physical cables, wireless sensors are easier to install, even in challenging or remote areas. Technicians can place them in large warehouses, separate rooms, or buildings with complex architecture more quickly and with fewer logistical challenges.
Reduced Cable-Related Issues:
Eliminating cables reduces the risk of cable-related problems such as damage, wear, or accidental disconnection. This leads to more reliable long-term operation and lower maintenance requirements.
Remote Monitoring and Real-Time Access:
Wireless temperature sensors can transmit data directly to monitoring systems via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or other wireless technologies. This enables real-time remote monitoring, which is especially valuable in industrial, agricultural, and smart home applications. Without cables to organize and troubleshoot, the setup remains uncluttered and less prone to physical interference.
HLY Technology Co., Ltd. Products
HLY Technology Co., Ltd. provides innovative wireless temperature sensors integrated into its data loggers. These products meet stringent requirements for protecting all types of supply chains, particularly cold chains. Ultimately, customers can select options suited for warehouses, laboratories, as well as sea, land, or air transportation. By integrating HLY’s data loggers into your operations, you can enhance service quality and maintain optimal conditions for sensitive goods, and encouraging customers to continue choosing your company as their trusted partner.
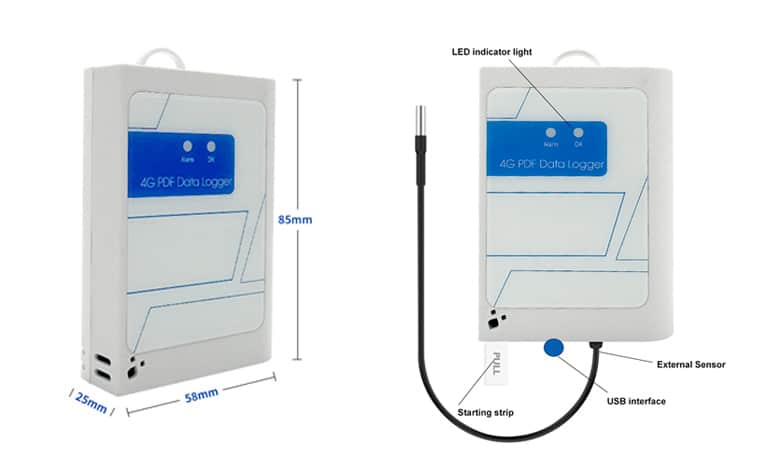
4G Real Time Disposable Temperature and Humidity Data Logger Size

